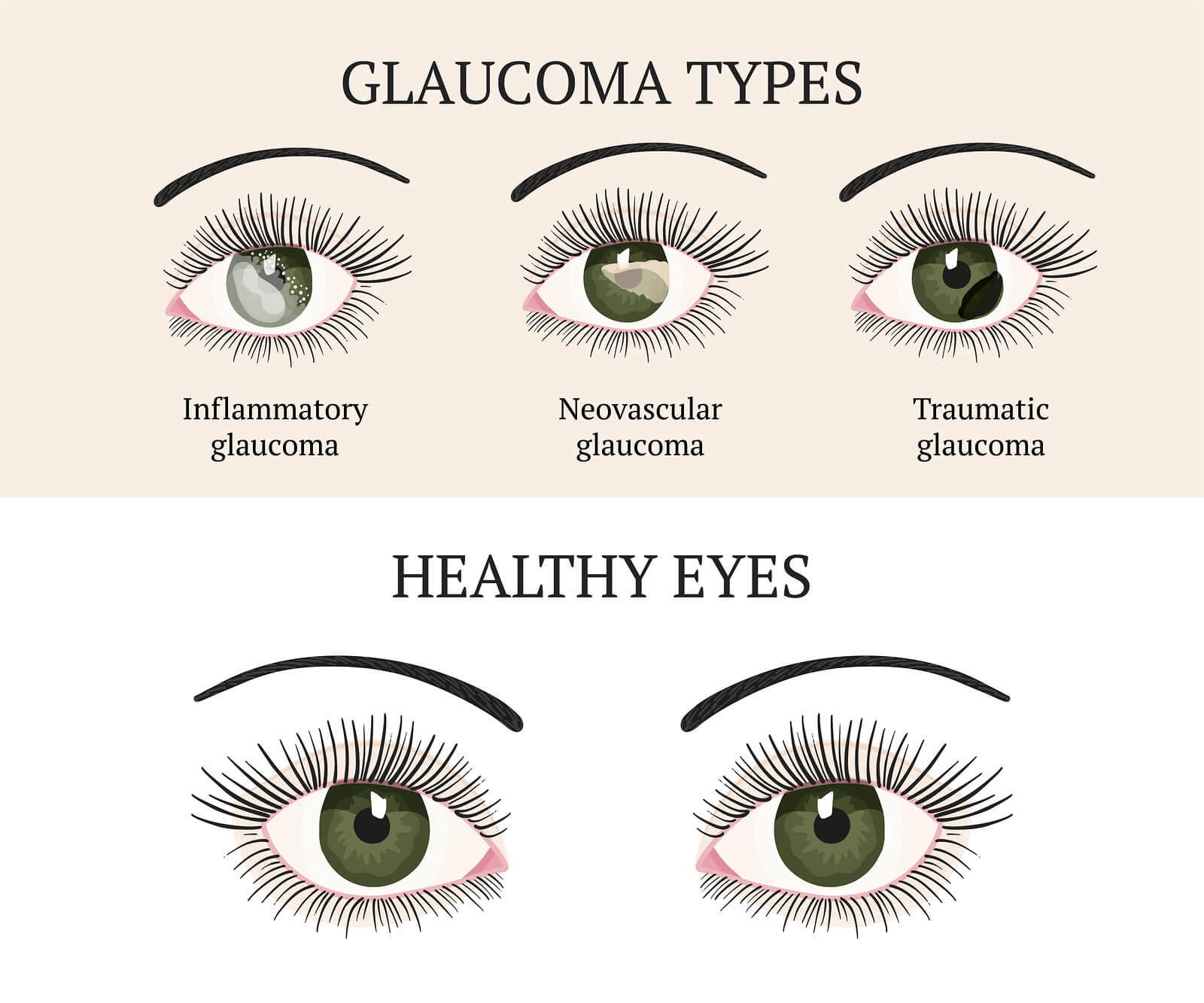
Formidable Info About How To Check For Glaucoma

You’re considered at high risk if at least one.
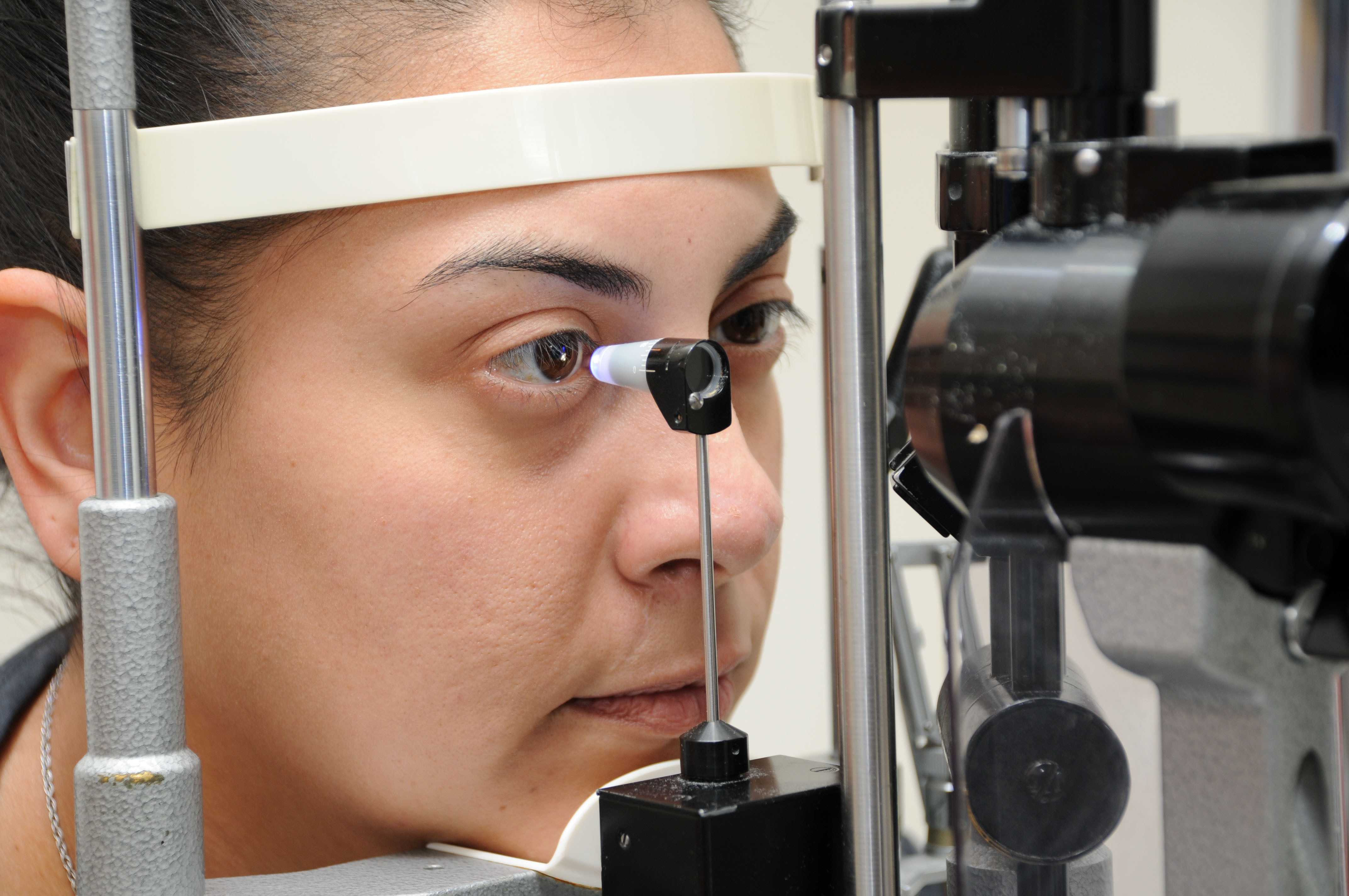
How to check for glaucoma. Checking the inner eye pressure testing the optic nerve testing the entire field of vision measuring the angle in the eye between the cornea and iris checking. The contact lens contains a mirror that can help the doctor see whether the space is blocked, or wide and open. Eye doctors can check for glaucoma as part of a comprehensive dilated eye exam.
Gonioscopy is a glaucoma test that uses a special mirrored device to gently touch the surface of the eye. The blood vessels that travel over the surface of the eye (the cornea). Gonioscopy examines the angle where the cornea meets the iris.
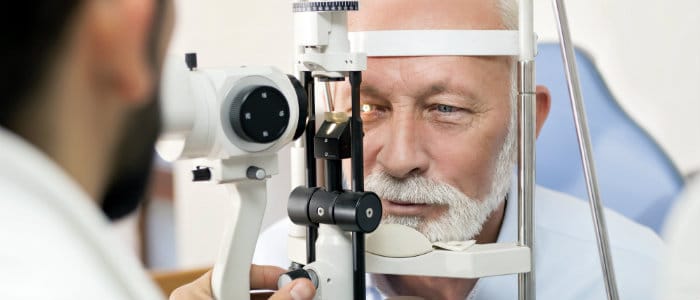
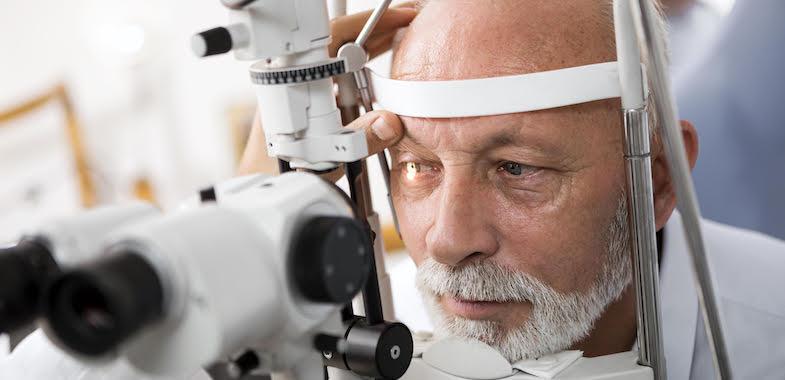
The test requires eye drops that anesthetize the eye, while a small device touches the eyeball to test the eye pressure. Medicare part b (medical insurance) covers glaucoma tests once every 12 months if you’re at high risk for developing the eye disease glaucoma. This diagnostic process allows your doctor to check for glaucoma damage in your optic nerve.
Eye drops dilate the pupil, allowing the doctor to check the structure and color of the optic. Next, your doctor will take a look at the back of your eye with a dilated eye. Tonometry measures the pressure within your eye.
Tests to diagnose and monitor glaucoma eye pressure test. An eye pressure test (tonometry) uses an instrument called a tonometer to measure the pressure inside. According to the glaucoma research foundation, the.
Its color and appearance can indicate whether or. Let’s discuss how an optometrist will test you for. The exam is simple and painless — your doctor will give you some eye drops to dilate (widen).
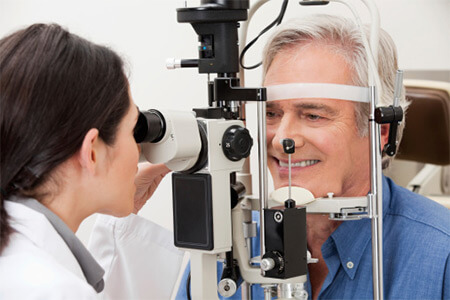
If your eye doctor suspects that you may have glaucoma, you will need to undergo additional testing that can help your doctor make a more definitive diagnosis of glaucoma: Your provider will use a device with a light and magnifying lens to look at your optic. To find out if you have glaucoma, eye doctors can use a few different tests—including a tonometry, ophthalmoscopy, gonioscopy—to help diagnose and find.
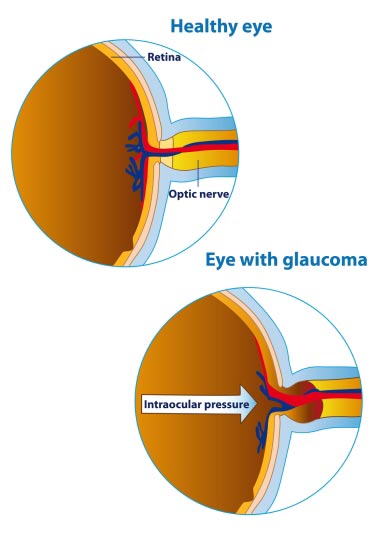
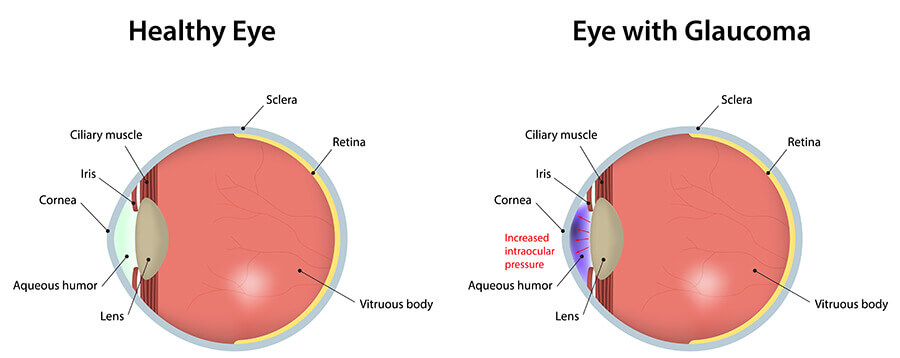
Using an instrument called an ophthalmoscope, your eye doctor can look directly through the pupil at the optic nerve.








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-585858357-56ac380e5f9b58b7d00a6c3a.jpg)